Save to My DOJO
In today’s world, disruption or outage of business operations directly translates to financial losses and a decrease in employee or customer satisfaction, and therefore, the urge for backup and disaster recovery has arisen. According to a report conducted by Consoltech, 70% of small businesses close within a year of a large data loss. Additionally, Statista, indicates that the global average cost of a data breach in 2022 was $4.35 million. Take a moment to let that sink in.
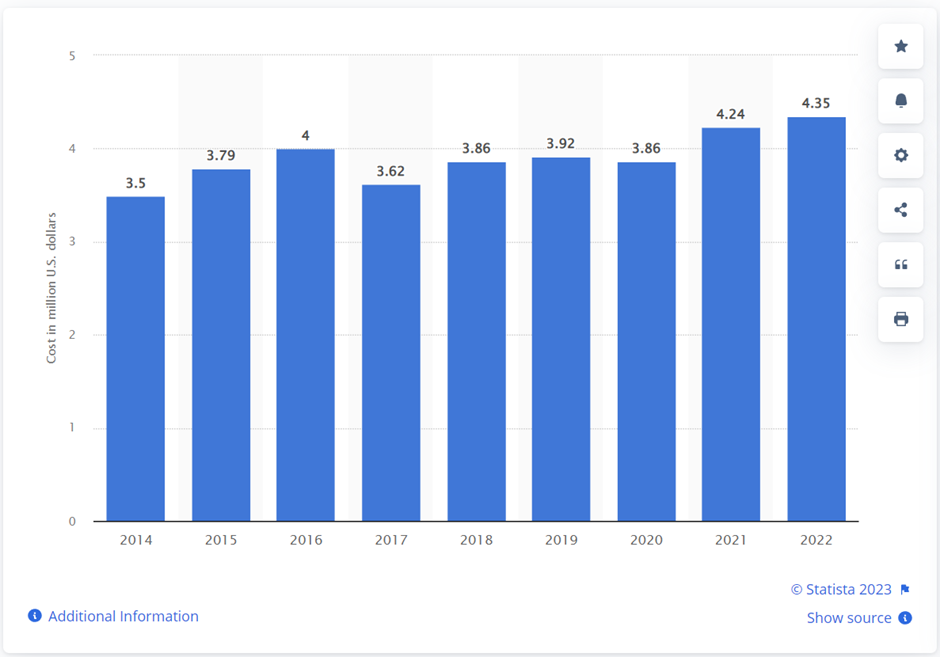
The average cost of a data breach worldwide from 2014 to 2022 (in million U.S. dollars)
When aiming to persuade the C-suite of the importance of the high availability of business services, the main argument would be around maintaining business continuity. All other supporting arguments that will be addressed in this article, directly derive from and contribute to its overarching importance.
This article focuses on backup and disaster recovery, providing an overview of common backup terms and presenting compelling arguments that can assist you in persuading the C-suite.
Let’s first clarify what backup and disaster recovery are.
The Difference Between Backups and Disaster Recovery
It is not uncommon for professionals to confuse backup and disaster recovery. Backup and disaster recovery are not synonymous, they are complementary for providing better data protection and business continuity in your infrastructure.
What is backup?
Backup is about creating copies of original files to one or more remote locations in your data center or into the cloud. Backup is an essential technology for any size company. In case of hardware or device failures, accidental deletion, data corruption, compromised data security, or even human error, you can easily restore data in a few clicks. Protect data and backup data matters, I think we can all agree.
What is disaster recovery?
On the other hand, Disaster Recovery (DR) is a set of processes and procedures that helps an organization restore its own service or data from outage to an operational state. Disaster recovery is relying on operational backup, sometimes augmented with real time data replication. For businesses that require continuous operation, it is crucial to have a proper disaster and recovery plan in place.
We have an article that explains backup and disaster recovery in detail. Be sure to read What is Backup and Disaster Recovery for Enterprise Computer Data.
Why is Backup and Recovery Important?
The importance of having backup and disaster recovery is directly proportional to the importance of keeping business services operational. That is probably the best argument that helps to determine the value of investing in backup and disaster recovery measures. Both backup and disaster recovery protect you against data failure.
There are different factors you can consider when talking about backup and recovery.

Why are backup and recovery important
Business continuity
As already mentioned, business continuity is a critical aspect that organizations must carefully consider. The end goal should be to recover quickly and reduce the impact on employees’ productivity, revenue, and customer satisfaction.
Risk mitigation
Risk mitigation is about being proactive and not reactive, validating all potential risks that can happen in your data center in case of a disaster, and properly addressing them.
Compliance and legal obligations
In some situations, depending on the type of business, some organizations are obliged to comply with compliance and legal obligations.
Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction and customer retention are one of the most important KPIs for the company’s growth. Do you want a happy customer? Then provide your services without disruption. Better customer satisfaction maintains a reputation. Happy customers attract more customers.
Competitive advantage
If services are operational that gives any company a competitive advantage compared to other companies.
Costs saving
All of the abovementioned aspects contribute to cost savings in the long term.
In honor of the initial publication of our free eBook; The Backup Bible, we extracted the top 10 most important messages from the book and compiled them into a handy reference. You can read them in The Ten Commandments of Backup.
How Successful Companies Backup Data
Let’s unpack each of them briefly.
Backup types
Data is referring to files, folders, virtual machines, databases, emails, or others. Once you select your data, you also need to select what kind of backup you want. You can select between incremental and differential backup. Incremental backup only changes made since the last backup, while differential backup since the last full backup.
If you feel you need more details about it, you can read our article Best Practices for Full, Differential, and Incremental Backup.
Backup location
In the next step, you define where you want to back up your data to. You can select between on-premises backup, cloud backup, and hybrid backup. On-premises backup involves backing up data within the organization’s (remote) data centers. This can include external hard disks, tape drives, and more commonly NAS (Network-Attached Storage).
If you don’t want to take care of management and maintenance of the on-premises storage devices, disk, scalability, or accessibility, then you can choose the cloud as your destination backup location. You can back up your data to AWS, Azure, Wasabi, and others.
You can also combine on-premises and cloud to hybrid backup. This way your data is better protected since it’s backed up to different locations that are geographically separated.
Location, Location, Location (Where to Back Up Data)!? Get an overview of the different storage options in the article Backup Storage Options and Size Requirements for Business.
Backup frequency and backup retention
In the next step, you need to define backup frequency and backup retention. Backup frequency defines how often you want to back up your data (e.g., each day at 3 AM UTC) and backup retention defines how long you want to keep your backup copies (e.g., keep it for one week). This has a direct effect on RPO and RTO which we will cover in the next section.
You can read more details about planning and scheduling in the article Backup Strategy – Best Practices: Planning and Scheduling and Backup and Recovery Tricks using Windows Task Scheduler.
Testing and monitoring
A backup is only considered successful if it can be successfully restored. In other words, you need to test your backup before you come into a situation where you need to use it. Another important aspect is the monitoring of your backup server. Monitoring can help you to check the health state of your backup server and backup jobs in your infrastructure, and get alerts when there are issues that need to be attended to.
RTO and RPO explained
RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) are two crucial metrics used in business continuity and disaster recovery. They help us to measure how quickly organizations can recover from outages and how much data loss can be tolerated.
RTO
The RTO (Recovery Time Objective) is about how long does organization can tolerate business disruption or downtime from ”it doesn’t work“, until it is restored to an operational state. RTO is typically measured in hours, minutes, and seconds, with the hope that it never extends to days.
RPO
On another hand, RPO (Recovery Point Objective) is the acceptance of data loss organizations can tolerate due to disruption or downtime. In regards to backup, it represents the timeframe from the last available and operational backup to the recovery point when the problem started.
Tourist agencies as an example
Let’s take a tourist agency as an example and imagine that the main booking server crashed due to an issue with the database, and all available booking dates and locations are lost. Tourist workers are unable to access any data, and customers are unable to make any bookings. The RTO would be how long it takes for the agency to restore the database to its operational state.
On the other hand, let’s say the agency is making backups every day. That means RPO is one day, and the tourist agency is willing to accept the data loss of one day. A shorter RPO, such as one hour, means that there is less potential data at risk or data that can be lost. The shorter the RPO, the better.

RTO and RPO explained
Hornetsecurity as Your Ultimate Partner in Backup and Disaster Recovery
You might have heard various new terms in this article and find yourself wondering which backup product to choose, one that includes all the aforementioned features, while being user-friendly. Fortunately you don’t have to look no further than Hornetsecurity VM Backup.
By using Hornetsecurity VM Backup you can back up your data to on-premises within your data center, or to the cloud, or make it a hybrid backup. This way you ensure data protection and operational service. Hornetsecurity VM Backup helps you to prioritize what workloads you want to back up.
Nearly everything, from servers to networks and applications, is being virtualized. If you are running your business workloads on VMware and Hyper-V, you can use Hornetsecurity VM Backup to securely back up and replicate your virtual machine’s critical data in your infrastructure.
The latest v9 release supports immutable protection against data loss and ransomware. You can start your free VM Backup trial today.
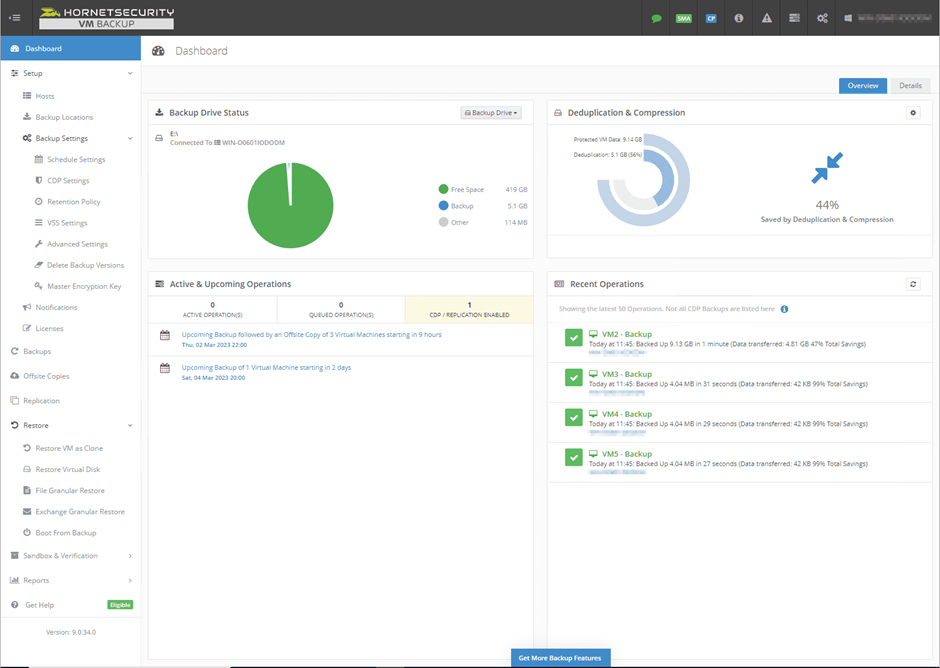
Back up and restore your company data with ease with Hornetsecurity VM
We work hard perpetually to give our customers confidence in their VM Backup, Spam & Malware Protection, Advanced Threat Protection, Email Encryption, Security Awareness Training, and Email Archiving strategies.
To keep up to date with the latest virtualization best practices, become a member of the Hornetsecurity blog now (it’s free). Join us in our passion for sharing content that helps you stay safe.
Wrap Up!
Any size company has one goal, to generate revenue by ensuring the high availability of their business services, maintaining employees’ productivity, and keeping customers happy.
To do so, having great products or services is important, but it is equally crucial to be proactive by using a proper backup and disaster recovery plan. Both backup and disaster recovery solutions are essential to protect your data, enhance data reliability, strengthen security measures, and enable effective response during complex disaster scenarios.
Backup helps organizations to create copies of their important files in safe locations in (remote) data centers and to the cloud, while disaster recovery is about processes and procedures that help organizations quickly restore failed services to an operational state.
You need them both. When choosing the proper backup tools there are several factors to consider. We addressed them all in this article. This article aims to provide an overview of basic terms related to backup and disaster recovery while equipping you with compelling arguments to engage in discussions with the C-suite.
Limited work tools rely on simply backing up data, making it imperative to have proper disaster recovery plans in place to handle unforeseen events effectively.

Not a DOJO Member yet?
Join thousands of other IT pros and receive a weekly roundup email with the latest content & updates!









