Save to My DOJO
Table of contents
- 1. Bring Your Own IP Address and Network Topology
- 2. Cross-Subnet Live Migration
- 3. VLANs Vs VSIDs
- 4. Run Multiple Virtual Networks on a Physical Network
- 5. Enable easier moves of Services to a Cloud
- 6. Move Virtual Machines across subnets and premises
- 7. Easy to setup with PowerShell or SCVMM
- 8. Compatibility with existing Network Devices
Hyper-V Network Virtualization technology, sometimes referred as HNV, is primarily designed to be used by the hosting providers, but every SMB should know the benefits offered by HNV.
Microsoft Hyper-V Network Virtualization is introduced with a new module called “WNV”. WNV stands for “Windows Network Virtualization”. The WNV module was first introduced with Windows Server 2012 as an additional component that you need to enable through running a PowerShell cmdlet before you can implement Hyper-V Network Virtualization functionality. Starting with Windows Server 2012 R2, the WNV module is integrated with the Hyper-V Virtual Switch, which means there is no need to run a PowerShell cmdlet in this version of Windows Server.
Hyper-V Network Virtualization is different from VMware’s NSX Network Virtualization. The objective is same but concept for implementing the Network Virtualization components is different. Hyper-V Network Virtualization was designed to address the limitations and complexity seen in typical environments using VLANs.
“Bring Your Own IP Address” is the main concern Hyper-V Network Virtualization addresses. Apart from that, HNV enables live migration of virtual machines across virtual subnets. Although these are the top reasons why HNV is adopted, there are a bunch of other benefits which Hyper-V Network Virtualization offers. Here’s the complete overview:
1. Bring Your Own IP Address and Network Topology
Customers can bring their own IP Addresses and Network Topologies without requiring any changes to the customer datacenter network. The isolation provided by the WNV policy makes it possible to host virtual machines with the same IP scheme on a Hyper-V Host. This is a great advantage for hosting providers. They can create policy rules to isolate customer virtual machines, while making sure customers communicate to their workloads using the same set of IP Addresses as they do in their local network.
2. Cross-Subnet Live Migration
Traditionally, live migration of virtual machines is limited to the same IP subnet or VLAN because crossing subnets required the virtual machine to change its IP address. This address change breaks existing communication and disrupts the services running on the virtual machine. With the help of HNV, it is now possible to live migrate virtual machines across different virtual subnets. HNV ensures that a live migrated virtual machine’s location is updated and synchronized among hosts that have ongoing communication with the migrated virtual machine. There are nothing changes with respect to the technologies used to live migrate virtual machines.
3. VLANs Vs VSIDs
Physical virtual switches can permit only 1000 VLANs out of 4096 IDs which is the maximum range. This range might not be sufficient for a hosting provider. Hyper-V Network Virtualization does not use VLAN IDs. It uses something called VSID which is part of WNV Module. The VSID is similar to VLAN IDs, but the range of VSIDs starts from 4096 to 16,777,214. Using VSIDs, you can have over 16 million virtual subnets created on a Hyper-V Host.
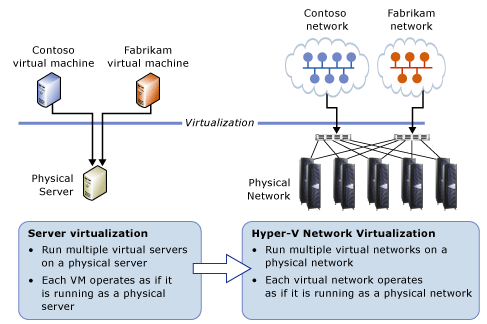
4. Run Multiple Virtual Networks on a Physical Network
As shown in the below figure, HNV enables hosting providers to run multiple virtual networks on a physical network with overlapping IP Addresses and each virtual network operates as it is the only virtual network running on the shared IaaS cloud.
5. Enable easier moves of Services to a Cloud
Since there are no changes required at the network layer and customers can bring their own IP Addresses, this enables IT organizations to move their datacenter services more easily without spending much time on the network planning.
6. Move Virtual Machines across subnets and premises
Virtual Machines can be moved to different virtual subnets or premises without requiring a change to the network topology. In case of any maintenance activity at one of the hosting sites, It is easy for hosting providers to relocate customer virtual machines to different data centers without any downtime and enable customers to access the virtual machines without any service disruption.
7. Easy to setup with PowerShell or SCVMM
You can either use HNV PowerShell cmdlets or SCVMM to implement HNV functionality. PowerShell cmdlets used to implement HNVs can be found here: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj884262.aspx. The Windows PowerShell cmdlets for Hyper-V Network Virtualization enable administrators to build command-line tools or automated scripts to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot network isolation policies. SCVMM is the core the datacenter management product designed to ease the deployment of HNV on multiple Hyper-V Servers.
8. Compatibility with existing Network Devices
The Hyper-V Network Virtualization technology does not require any changes to the network devices and can successfully be implemented in today’s datacenter. The overall goal of the Hyper-V Network Virtualization is to ensure customers can bring their own IP Addresses and network topologies and enable easier move of customer workloads to a shared IaaS cloud. Hosting providers can run customer virtual machines with same IP Scheme and these vrtual machines can be live migrated without requiring any disruption to the service.
You can read more about Hyper-V Network Virtualization here: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj134174.aspx.

Not a DOJO Member yet?
Join thousands of other IT pros and receive a weekly roundup email with the latest content & updates!