Save to My DOJO
One of the reasons I enjoy working with PowerShell is that once you understand the fundamentals and have gained some scripting experience you can use it to manage almost anything. It is even easier when the “thing” you want to manage offers a set of PowerShell commands. Because I need Hyper-V to maintain my test and development environment, it is very important that I keep on top of it. If you’ve been reading my contributions to this blog over the years you’ll recognize that I take advantage of PowerShell to manage Hyper-V where ever I can. My latest tool is a PowerShell function that gives me a snapshot view of the state of a Hyper-V host.
The Building Blocks
The function will assemble a composite object from a collection of information pulled from a variety of sources. Internally, the function is taking advantage of Get-VM, Get-VMHost, Get-Volume, Get-Ciminstance and Get-Counter. My expectation is that you will be running this command from your Windows 10 desktop to remotely query a Hyper-V server. I’m also assuming you are running a relatively recent version of Hyper-V and a Windows Server operating system. Although I have not tested this with Windows Server 2019.
The best part is that you don’t need the Hyper-V PowerShell tools installed locally on your desktop because the function uses PowerShell remoting, via Invoke-Command, to get all of the information it needs to provide the status object. By using PowerShell remoting this also makes it easier to query multiple remote servers at the same time since the data gathering code runs on the remote servers more or less simultaneously. Naturally, this assumes you have enabled PowerShell remoting on your Hyper-V server, and there’s no reason not to. You also need a credential with admin rights on the remote Hyper-V server. But I provided a parameter in my function to let you specify an alternate credential.
I assumed most of you would specify a remote computer by name, but I also provided a way to use an existing PSSession object. There is always a little overhead when you use Invoke-Command in setting up the PSSession connection so if you already have a PSSession object that will speed things up a bit.
Performance Counter Data
I’ve written a fair amount lately on working with Hyper-V performance counters in PowerShell. My status tool also uses a number of performance counters.
$counters = Get-Counter -counter 'processor(_total)% processor time', 'hyper-v virtual machine health summaryhealth critical', 'hyper-v virtual machine health summaryhealth ok', "hyper-v virtual switch(*)bytes/sec", "hyper-v virtual switch(*)packets/sec", 'systemprocesses', 'hyper-v hypervisor logical processor(_total)% guest run time', 'hyper-v hypervisor logical processor(_total)% hypervisor run time'
You might want to edit this list and to include counters that matter to you. One thing you will need to do is modify the custom object to reflect the counter value. As an example here’s the first part of the custom object.
[pscustomobject]@{
Computername = $vHost.Name
Uptime = (Get-Date) - $os.LastBootUpTime
PctProcessorTime = _getCooked -sample $counters.countersamples -counter '% processor time'
I am defining a property called PctProcessorTime pulling the value from the countersample property. In order to keep my code better organized, I created a short “helper” function called _getCooked to process the countersample.
Function _getCooked {
Param(
[Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.GetCounter.PerformanceCounterSample[]]$Sample,
[string]$Counter
)
(($Sample).where( {$_.path -match "$counter"})).cookedValue
} #close _getCooked
The function is nested inside the scriptblock that will run remotely. I am intentionally using a non-standard name since this function is not publicly exposed. The function filters the counter sample looking for a specific counter name and returns the cooked value. As you look through the finished code below you’ll see I invoke this function repeatedly. If I need to fix something I only have to fix it in one place. if you modify the function to return different performance counter data you can use the function to retrieve the cooked values.
Other Data
The other data is pulled from a variety of commands like Get-VMHost and Get-Volume. In my status tool, I wanted to know how much space remains on the volume that contains the default virtual hard disk path.
$vol = Get-Volume (Split-Path $vhost.VirtualHardDiskPath).Substring(0, 1) -ErrorAction Stop
And because I’m gathering a lot of information my function uses Write-Progress to provide feedback.
Here’s how it all comes together.
Get-VMHostStatus
#requires -version 5.1
Function Get-VMHostStatus {
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Get a summary of a Hyper-V Host
.DESCRIPTION
Use this command to get a summary snapshot of a Hyper-V Host. The command uses PowerShell remoting to gather system information, performance counter data and Hyper-V settings. It does not require the Hyper-V module unless you are running it on the local host, which is the default.
.PARAMETER Computername
Enter the name of the Hyper-V host.
.PARAMETER Credential
Enter an alternate credential in the form domainusername or machineusername.
.EXAMPLE
PS C:> Get-VMHostStatus -Computername HV01
Computername : HV01
Uptime : 13.20:01:31.7222927
PctProcessorTime : 18.1370520347218
TotalMemoryGB : 128
PctMemoryFree : 34.79
TotalVMs : 24
RunningVMs : 18
OffVMs : 5
SavedVMs : 0
PausedVMs : 1
OtherVMs : 0
Critical : 0
Healthy : 24
TotalAssignedMemoryGB : 32.896484375
TotalDemandMemoryGB : 20.80078125
TotalPctDemand : 18.18
PctFreeDisk : 47.5408662499084
VMSwitchBytesSec : 926913.772872509
VMSwitchPacketsSec : 24.98692048485236
LogicalProcPctGuestRuntime : 12.15894683010222
LogicalProcPctHypervisorRuntime : 2.710086619427829
TotalProcesses : 271
.INPUTS
System.String
.OUTPUTS
Custom object
.LINK
Get-Counter
.lINK
Get-VMHost
.LINK
Get-Volume
.LINK
Get-VM
.LINK
Invoke-Command
#>
[cmdletbinding(DefaultParameterSetName = "Computername")]
Param(
[Parameter(Position = 0, Mandatory, ValueFromPipeline, ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName, HelpMessage = "Enter the name of the Hyper-V host.", ParameterSetName = "Computername")]
[ValidateNotNullorEmpty()]
[string[]]$Computername,
[Parameter(ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName, HelpMessage = "Enter an alternate credential in the form domainusername or machineusername.", ParameterSetName = "Computername")]
[PSCredential]$Credential,
[Parameter(ParameterSetName = "Computername")]
[ValidateSet('Default', 'Basic', 'Credssp', 'Digest', 'Kerberos', 'Negotiate', 'NegotiateWithImplicitCredential')]
[ValidateNotNullorEmpty()]
[string]$Authentication = "default",
[Parameter(ParameterSetName = "Computername")]
[switch]$UseSSL,
[Parameter(ParameterSetName = "Computername")]
[System.Management.Automation.Remoting.PSSessionOption]$SessionOption,
[Parameter(Position = 0,ParameterSetName = "session", ValueFromPipeline)]
[System.Management.Automation.Runspaces.PSSession[]]$Session
)
Begin {
Write-Verbose "[BEGIN ] Starting: $($MyInvocation.Mycommand)"
$progParams = @{
Activity = $MyInvocation.MyCommand
Status = "Preparing..."
CurrentOperation = ""
PercentComplete = 0
}
if (-not $PSBoundParameters.ContainsKey("ErrorAction")) {
$PSBoundParameters.add("ErrorAction", "Stop")
}
#get all the data via a remote scriptblock
$sb = {
#define a nested function to parse counter samples
Function _getCooked {
Param(
[Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.GetCounter.PerformanceCounterSample[]]$Sample,
[string]$Counter
)
(($Sample).where( {$_.path -match "$counter"})).cookedValue
} #close _getCooked
Try {
($using:progParams).CurrentOperation = "Getting VMHost"
($using:progParams).PercentComplete = 20
Write-Progress @using:progparams
$vHost = Get-VMHost -ErrorAction stop
($using:progParams).CurrentOperation = "Getting OS properties"
($using:progParams).PercentComplete = 30
Write-Progress @using:progParams
$os = Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_OperatingSystem -property LastBootUpTime, FreePhysicalMemory, TotalVisibleMemorySize -ErrorAction Stop
#get volume with default virtual hard disk path to check space
($using:progParams).CurrentOperation = "Getting virtual hard disk path volume"
($using:progParams).PercentComplete = 40
Write-Progress @using:progParams
$vol = Get-Volume (Split-Path $vhost.VirtualHardDiskPath).Substring(0, 1) -ErrorAction Stop
($using:progParams).CurrentOperation = "Getting virtual machines"
($using:progParams).PercentComplete = 60
Write-Progress @using:progParams
$vms = Get-VM
($using:progParams).CurrentOperation = "Calculating VM Usage"
($using:progParams).PercentComplete = 75
Write-Progress @using:progParams
$vmusage = ($vms).Where( {$_.state -eq 'running'}) | Select-Object Name,
@{Name = "Status"; Expression = {$_.MemoryStatus}},
@{Name = "MemAssignGB"; Expression = {$_.MemoryAssigned / 1GB}},
@{Name = "PctAssignTotal"; Expression = {[math]::Round(($_.memoryAssigned / ($vhost.memoryCapacity)) * 100, 2)}},
@{Name = "MemDemandGB"; Expression = {$_.MemoryDemand / 1GB}},
@{Name = "PctDemandTotal"; Expression = {[math]::Round(($_.memoryDemand / ($vhost.MemoryCapacity)) * 100, 2)}}
#get performance counter data
($using:progParams).CurrentOperation = "Getting performance counter data"
($using:progParams).PercentComplete = 80
Write-Progress @using:progParams
$counters = Get-Counter -counter 'processor(_total)% processor time',
'hyper-v virtual machine health summaryhealth critical',
'hyper-v virtual machine health summaryhealth ok',
"hyper-v virtual switch(*)bytes/sec",
"hyper-v virtual switch(*)packets/sec",
'systemprocesses',
'hyper-v hypervisor logical processor(_total)% guest run time',
'hyper-v hypervisor logical processor(_total)% hypervisor run time'
#write result as a custom object
[pscustomobject]@{
Computername = $vHost.Name
Uptime = (Get-Date) - $os.LastBootUpTime
PctProcessorTime = _getCooked -sample $counters.countersamples -counter '% processor time'
TotalMemoryGB = $vhost.MemoryCapacity / 1GB -as [int]
PctMemoryFree = [Math]::Round(($os.FreePhysicalMemory / $os.totalVisibleMemorySize) * 100, 2)
TotalVMs = $vms.count
RunningVMs = $vms.where( {$_.state -eq 'running'}).count
OffVMs = $vms.where( {$_.state -eq 'off'}).count
SavedVMs = $vms.where( {$_.state -eq 'Saved'}).count
PausedVMs = $vms.where( {$_.state -eq 'Paused'}).count
OtherVMs = $vms.where( {$_.state -notmatch "running|off|saved|Paused"}).count
Critical = _getCooked -sample $counters.CounterSamples -counter "health critical"
Healthy = _getCooked -sample $counters.countersamples -counter 'health ok'
TotalAssignedMemoryGB = ($vmusage | Measure-Object -Property MemAssignGB -sum).sum
TotalDemandMemoryGB = ($vmusage | Measure-Object -Property MemDemandGB -sum).sum
TotalPctDemand = ($vmusage | Measure-Object -Property PctDemandTotal -sum).sum
PctFreeDisk = ($vol.SizeRemaining / $vol.size) * 100
VMSwitchBytesSec = (_getCooked -sample $counters.countersamples -counter 'bytes/sec' | Measure-Object -sum).sum
VMSwitchPacketsSec = (_getCooked -sample $counters.countersamples -counter 'packets/sec' | Measure-Object -sum).sum
LogicalProcPctGuestRuntime = _getCooked -sample $counters.countersamples -counter 'guest run time'
LogicalProcPctHypervisorRuntime = _getCooked -sample $counters.countersamples -counter 'hypervisor run time'
TotalProcesses = _getCooked -sample $counters.countersamples -counter '\system\processes'
}
} #try
catch {
Throw $_
} #catch
} #close scriptblock
} #begin
Process {
Write-Verbose "[PROCESS] Using parameter set $($pscmdlet.ParameterSetName)"
If ($PSCmdlet.ParameterSetName -eq 'session') {
$ps = $Session
}
else {
Try {
Write-Verbose "[PROCESS] Creating a PSSession to $($Computername -join ',')"
$progParams.CurrentOperation = "Creating temporary PSSession"
$progParams.PercentComplete = 5
Write-Progress @progParams
$ps = New-PSSession @PSBoundParameters
#define a variable to indicate these sessions were created on an ad hoc basis
#so they can be removed.
$adhoc = $True
}
Catch {
Throw $_
#make sure we bail out is the session can't be created
Return
}
}
foreach ($session in $ps) {
Write-Verbose "[PROCESS] Querying $($session.computername.toUpper())"
$progParams.status = $session.computername.toUpper()
$progParams.CurrentOperation = "Invoking scriptblock"
$progParams.PercentComplete = 10
Write-Progress @progParams
Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock $sb -Session $session -HideComputerName |
Select-Object -Property * -ExcludeProperty RunspaceID, PSShowComputername, PSComputername
} #foreach
} #process
End {
$progParams.CurrentOperation = "Cleaning up"
$progParams.PercentComplete = 95
Write-Progress @progParams
if ($adhoc) {
Write-Verbose "[END ] Cleaning up sessions"
Remove-PSSession $ps
}
Write-Verbose "[END ] Ending: $($MyInvocation.Mycommand)"
} #end
} #close function
You will need to dot source the script file into your PowerShell session.
. c:scriptsget-vmhoststatus.ps1
I’ve taken the liberty of providing help.
To run it, all you need to do at a minimum is specify the name of the Hyper-V host.
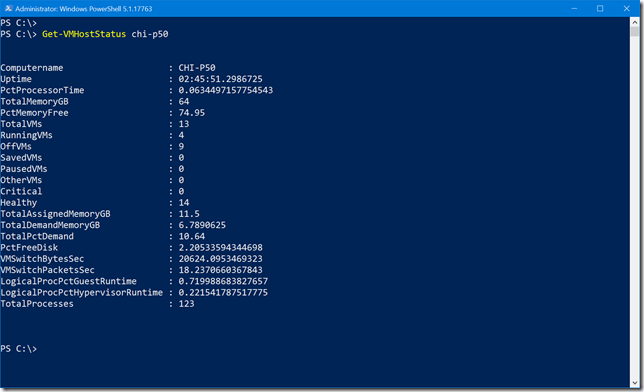
In looking at the output I can see that I only have about 2% free disk space remaining! Guess I’d better take a look at that.
This function acts like any other PowerShell command, even querying multiple servers.
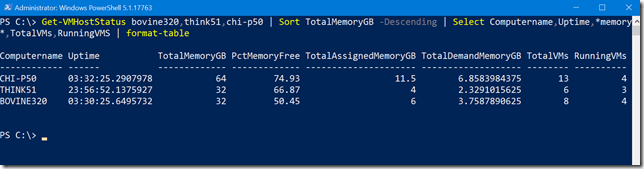
But Wait There’s More
With a little bit of effort on my part, I now have a re-usable PowerShell tool I can run anytime to produce a detailed look at the health and status of a Hyper-V host. Even better, I can use this function as the core for other PowerShell projects. I’ll share a few of those next time. In the meantime, I hope you’ll grab the code and give it a spin.

Not a DOJO Member yet?
Join thousands of other IT pros and receive a weekly roundup email with the latest content & updates!








21 thoughts on "Building a Hyper-V Host Status Tool with PowerShell"
GReat Script….my compliment 🙂
PS C:> Get-VMHostStatus servername
Get-VMHostStatus : The term ‘Get-VMHostStatus’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or
operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try
again.
At line:1 char:1
Get-VMHostStatus servername
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
CategoryInfo : ObjectNotFound: (Get-VMHostStatus:String) [], CommandNotFoundException
FullyQualifiedErrorId : CommandNotFoundException
You need to load the function I wrote into your PowerShell session. As currently written you would need to save it to a ps1 file on your computer. Then dot source the ps1 file in your PowerShell session.
PS C:> . c:scriptsyourfile.ps1
PS C:> help get-vmhoststatus
Great script Jeffrey. Do you have any advice on why it doesn’t run for me though? I’ve tried it on several HV hosts (PS 5.1), and it doesn’t do anything. No errors at all. help get-vmhoststatus does error though. I’ve tried it with just server name as well as using the ‘-computername’ option. Still nothing.
Did you dot source the script file? See my comment below.